---
uid: urp-create-custom-renderer-feature
---
# Example of a complete Scriptable Renderer Feature
This section describes how to create a complete [Scriptable Renderer Feature](./scriptable-renderer-features/intro-to-scriptable-renderer-features.md) for a URP Renderer.
This walkthrough contains the following sections:
* [Overview of this example implementation](#example-implementation-overview)
* [Create example Scene and GameObjects](#example-scene)
* [Create a scriptable Renderer Feature and add it to the Universal Renderer](#scriptable-renderer-feature)
* [Add the Renderer Feature to the the Universal Renderer asset](#add-renderer-feature-to-asset)
* [Create the scriptable Render Pass](#scriptable-render-pass)
* [Implement the settings for the custom render pass](#implement-the-settings-for-the-custom-render-pass)
* [Implement the render passes](#implement-the-render-passes)
* [Enqueue the render pass in the custom renderer feature](#enqueue-the-render-pass-in-the-custom-renderer-feature)
* [Implement the volume component](#volume-component)
* [All complete code for the scripts in this example](#all-complete-code-for-the-scripts-in-this-example)
* [Custom Renderer Feature code](#code-renderer-feature)
* [Custom render pass code](#code-render-pass)
* [Volume Component code](#code-volume-component)
* [The custom shader for the blur effect](#example-shader)
## Overview of this example implementation
The example workflow on this page implements a custom Renderer Feature that uses [custom Render Passes](./intro-to-scriptable-render-passes.md) to add a blur effect to the camera output.
The implementation consists of the following parts:
* A `ScriptableRendererFeature` instance that enqueues a `ScriptableRenderPass` instance every frame.
* A `ScriptableRenderPass` instance that performs the following steps:
* Creates a temporary render texture using the `RenderTextureDescriptor` API.
* Applies two passes of the [custom shader](#example-shader) to the camera output using the `TextureHandle` and the `Blitter` API.
## Create example Scene and GameObjects
To set your project up for this example workflow:
1. Create a new Scene.
1. Create two GameObjects: a Cube GameObject called `Cube`, and a Sphere GameObject called `Sphere`.
2. Create two Materials with a shader that lets you specify the base color (for example, the `Universal Render Pipeline/Lit` shader). Call the Materials `Blue` and `Red`, and set the base colors of the Materials to blue and red respectively.
3. Assign the `Red` Material to the cube and the `Blue` Material to the sphere.
3. Position the camera so that it has the cube and the sphere in its view.
4. In the URP Asset, set the property **Quality** > **Anti Aliasing (MSAA)** to **Disabled**. The purpose of this step is to simplify the example implementation.
The sample scene should look like the following image:

## Create a scriptable Renderer Feature and add it to the Universal Renderer
1. Create a new C# script and name it `BlurRendererFeature.cs`.
2. In the script, remove the code that Unity inserted in the `BlurRendererFeature` class.
3. Add the following `using` directive:
```C#
using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal;
```
3. Create the `BlurRendererFeature` class that inherits from the **ScriptableRendererFeature** class.
```C#
public class BlurRendererFeature : ScriptableRendererFeature
```
4. In the `BlurRendererFeature` class, implement the following methods:
* `Create`: Unity calls this method on the following events:
* When the Renderer Feature loads the first time.
* When you enable or disable the Renderer Feature.
* When you change a property in the inspector of the Renderer Feature.
* `AddRenderPasses`: Unity calls this method every frame, once for each camera. This method lets you inject `ScriptableRenderPass` instances into the scriptable Renderer.
Now you have the custom `BlurRendererFeature` Renderer Feature with its main methods.
Below is the complete code for this step.
```C#
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal;
public class BlurRendererFeature : ScriptableRendererFeature
{
public override void Create()
{
}
public override void AddRenderPasses(ScriptableRenderer renderer,
ref RenderingData renderingData)
{
}
}
```
### Add the Renderer Feature to the the Universal Renderer asset
Add the Renderer Feature you created to the the Universal Renderer asset. For information on how to do this, refer to the page [How to add a Renderer Feature to a Renderer](../urp-renderer-feature-how-to-add.md).
## Create the scriptable Render Pass
This section demonstrates how to create a scriptable Render Pass and enqueue its instance into the scriptable Renderer.
1. Create a new C# script and name it `BlurRenderPass.cs`.
2. In the script, remove the code that Unity inserted in the `BlurRenderPass` class. Add the following `using` directive:
```C#
using UnityEngine.Rendering;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.RenderGraphModule;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal;
```
3. Create the `BlurRenderPass` class that inherits from the **ScriptableRenderPass** class.
```C#
public class BlurRenderPass : ScriptableRenderPass
```
4. Add the `RecordRenderGraph` method to the class. This method adds and configures render passes in the render graph. This process includes declaring render pass inputs and outputs, but does not include adding commands to command buffers. Unity calls this method every frame, once for each camera.
```C#
public override void RecordRenderGraph(RenderGraph renderGraph, ContextContainer frameData)
{ }
```
Below is the complete code for the `BlurRenderPass.cs` file from this section.
```C#
using UnityEngine.Rendering;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.RenderGraphModule;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal;
public class BlurRenderPass : ScriptableRenderPass
{
public override void RecordRenderGraph(RenderGraph renderGraph,
ContextContainer frameData)
{
}
}
```
## Implement the settings for the custom render pass
This section demonstrates how to implement the settings for the custom blur render pass.
1. The Renderer Feature in this example uses the [shader](#example-shader) that performs the blur horizontally in one pass, and vertically in another pass. To let users control the blur value for each pass, add the following `BlurSettings` class to the `BlurRendererFeature.cs` script.
```C#
[Serializable]
public class BlurSettings
{
[Range(0,0.4f)] public float horizontalBlur;
[Range(0,0.4f)] public float verticalBlur;
}
```
2. In the `BlurRendererFeature` class, declare the following fields:
```C#
[SerializeField] private BlurSettings settings;
[SerializeField] private Shader shader;
private Material material;
private BlurRenderPass blurRenderPass;
```
3. In the `BlurRenderPass` class, add the fields for the settings, the Material, and the constructor that uses those fields.
```C#
private BlurSettings defaultSettings;
private Material material;
public BlurRenderPass(Material material, BlurSettings defaultSettings)
{
this.material = material;
this.defaultSettings = defaultSettings;
}
```
4. In the `BlurRenderPass` class, add the `RenderTextureDescriptor` field and initialize it in the constructor. The `RenderTextureDescriptor` class lets you specify the properties of a render texture, such as the width, height, and format.
```C#
using UnityEngine;
private RenderTextureDescriptor blurTextureDescriptor;
public BlurRenderPass(Material material, BlurSettings defaultSettings)
{
this.material = material;
this.defaultSettings = defaultSettings;
blurTextureDescriptor = new RenderTextureDescriptor(Screen.width, Screen.height,
RenderTextureFormat.Default, 0);
}
```
5. In the `BlurRenderPass` class, declare the `PassData` class for storing the render pass input data. The `RecordRenderGraph` method populates the data and the render graph passes it as a parameter to the rendering function. The `TextureHandle` field stores the reference to the temporary input texture.
```C#
private class PassData
{
internal TextureHandle src;
internal Material material;
}
```
5. In the `RecordRenderGraph` method, create the variable for storing the `UniversalResourceData` instance from the `frameData` parameter. `UniversalResourceData` contains all the texture references used by URP, including the active color and depth textures of the camera.
```C#
UniversalResourceData resourceData = frameData.Get();
```
6. Declare the variables for interacting with the shader properties.
```C#
private static readonly int horizontalBlurId = Shader.PropertyToID("_HorizontalBlur");
private static readonly int verticalBlurId = Shader.PropertyToID("_VerticalBlur");
private const string k_BlurTextureName = "_BlurTexture";
private const string k_VerticalPassName = "VerticalBlurRenderPass";
private const string k_HorizontalPassName = "HorizontalBlurRenderPass";
```
6. In the `RecordRenderGraph` method, declare the `TextureHandle` fields to store the references to the input and the output textures. `CreateRenderGraphTexture` is a helper method that calls the `RenderGraph.CreateTexture` method.
```C#
TextureHandle srcCamColor = resourceData.activeColorTexture;
TextureHandle dst = UniversalRenderer.CreateRenderGraphTexture(renderGraph, blurTextureDescriptor, k_BlurTextureName, false);
```
7. In the `BlurRenderPass` class, implement the `UpdateBlurSettings` method that updates the shader values.
```C#
private void UpdateBlurSettings()
{
if (material == null) return;
// Use the Volume settings or the default settings if no Volume is set.
var volumeComponent =
VolumeManager.instance.stack.GetComponent();
float horizontalBlur = volumeComponent.horizontalBlur.overrideState ?
volumeComponent.horizontalBlur.value : defaultSettings.horizontalBlur;
float verticalBlur = volumeComponent.verticalBlur.overrideState ?
volumeComponent.verticalBlur.value : defaultSettings.verticalBlur;
material.SetFloat(horizontalBlurId, horizontalBlur);
material.SetFloat(verticalBlurId, verticalBlur);
}
```
8. In the `RecordRenderGraph` method, add the variable for storing the `UniversalCameraData` data, and set the `RenderTextureDescriptor` values using that data.
```C#
UniversalCameraData cameraData = frameData.Get();
// The following line ensures that the render pass doesn't blit
// from the back buffer.
if (resourceData.isActiveTargetBackBuffer)
return;
// Set the blur texture size to be the same as the camera target size.
blurTextureDescriptor.width = cameraData.cameraTargetDescriptor.width;
blurTextureDescriptor.height = cameraData.cameraTargetDescriptor.height;
blurTextureDescriptor.depthBufferBits = 0;
```
8. In the `RecordRenderGraph` method, add the function to continuously update the blur settings in the material.
```C#
// Update the blur settings in the material
UpdateBlurSettings();
// This check is to avoid an error from the material preview in the scene
if (!srcCamColor.IsValid() || !dst.IsValid())
return;
```
## Implement the render passes
1. In the `RecordRenderGraph` method, using the `builder` variable, add the render pass for the vertical blur. The `SetRenderFunc` method sets the rendering function for the render pass. In this example, the function blits the camera color to the render graph texture, using the first shader pass.
```C#
// Vertical blur pass
using (var builder = renderGraph.AddRasterRenderPass(k_VerticalPassName,
out var passData))
{
// Configure pass data
passData.src = srcCamColor;
passData.material = material;
// Configure render graph input and output
builder.UseTexture(passData.src);
builder.SetRenderAttachment(dst, 0);
// Blit from the camera color to the render graph texture,
// using the first shader pass.
builder.SetRenderFunc((PassData data, RasterGraphContext context) => ExecutePass(data, context, 0));
}
```
The `BlitTexture` method uses the `m_ScaleBias` argument. add it in the `BlurRenderPass` class.
```C#
private Vector4 m_ScaleBias = new Vector4(1f, 1f, 0f, 0f);
```
2. In the `RecordRenderGraph` method, using the `builder` variable, add the render pass for the horizontal blur. This pass uses the output of the previous pass as its input. Refer to the complete shader code for the implementation details.
```C#
// Horizontal blur pass
using (var builder = renderGraph.AddRasterRenderPass(k_HorizontalPassName, out var passData))
{
// Configure pass data
passData.src = dst;
passData.material = material;
// Use the output of the previous pass as the input
builder.UseTexture(passData.src);
// Use the input texture of the previous pass as the output
builder.SetRenderAttachment(srcCamColor, 0);
// Blit from the render graph texture to the camera color,
// using the second shader pass.
builder.SetRenderFunc((PassData data, RasterGraphContext context) => ExecutePass(data, context, 1));
}
```
The complete code for this part is in section [Custom render pass code](#code-render-pass).
## Enqueue the render pass in the custom renderer feature
In this section, you instantiate the render pass in the `Create` method of the `BlurRendererFeature` class, and enqueue it in the `AddRenderPasses` method.
1. In the `Create` method of the `BlurRendererFeature` class, instantiate the `BlurRenderPass` class.
In the method, use the `renderPassEvent` field to specify when to execute the render pass.
```C#
public override void Create()
{
if (shader == null)
{
return;
}
material = new Material(shader);
blurRenderPass = new BlurRenderPass(material, settings);
blurRenderPass.renderPassEvent = RenderPassEvent.AfterRenderingSkybox;
}
```
2. In the `AddRenderPasses` method of the `BlurRendererFeature` class, enqueue the render pass with the `EnqueuePass` method.
```C#
public override void AddRenderPasses(ScriptableRenderer renderer, ref RenderingData renderingData)
{
if (renderingData.cameraData.cameraType == CameraType.Game)
{
renderer.EnqueuePass(blurRenderPass);
}
}
```
3. Implement the `Dispose` method that destroys the material instance that the Renderer Feature creates.
```C#
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
#if UNITY_EDITOR
if (EditorApplication.isPlaying)
{
Destroy(material);
}
else
{
DestroyImmediate(material);
}
#else
Destroy(material);
#endif
}
```
For the complete Renderer Feature code, refer to section [Custom Renderer Feature code](#code-renderer-feature).
The Scriptable Renderer Feature is now complete. The following image shows the effect of the feature in the Game view and the example settings.
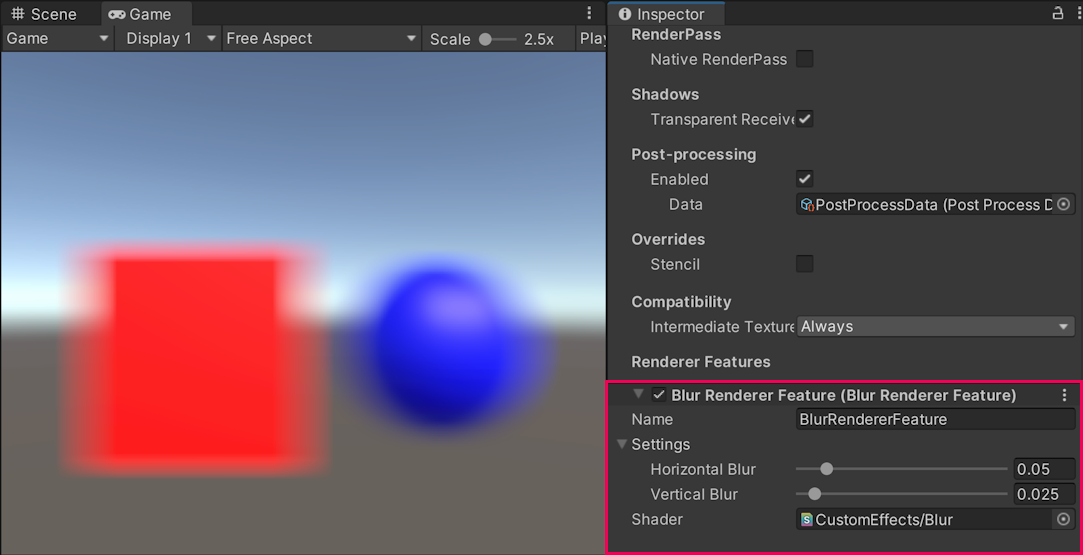
*The effect of the Scriptable Renderer Feature in the Game view.*
## Implement the volume component
This section shows how to implement a volume component that lets you control the input values for the custom renderer feature.
1. Create a new C# script and name it `CustomVolumeComponent.cs`.
1. Inherit the `CustomVolumeComponent` class from the `VolumeComponent` class, add the `[Serializable]` attribute to the class. Add the `using UnityEngine.Rendering;` directive.
```C#
using System;
using UnityEngine.Rendering;
[Serializable]
public class CustomVolumeComponent : VolumeComponent
{
}
```
2. Add the `BoolParameter` field to the `CustomVolumeComponent` class. This field lets you enable or disable the custom renderer feature.
```C#
public class BlurVolumeComponent : VolumeComponent
{
public BoolParameter isActive = new BoolParameter(true);
}
```
3. Add the fields to control the blur settings defined in the custom renderer feature.
```C#
[Serializable]
public class CustomVolumeComponent : VolumeComponent
{
public BoolParameter isActive = new BoolParameter(true);
public ClampedFloatParameter horizontalBlur =
new ClampedFloatParameter(0.05f, 0, 0.5f);
public ClampedFloatParameter verticalBlur =
new ClampedFloatParameter(0.05f, 0, 0.5f);
}
```
4. In the `BlurRenderPass` script, change the `UpdateBlurSettings` method so that it uses the settings defined in a Volume or the default settings if no Volume is set.
```C#
private void UpdateBlurSettings()
{
if (material == null) return;
// Use the Volume settings or the default settings if no Volume is set.
var volumeComponent =
VolumeManager.instance.stack.GetComponent();
float horizontalBlur = volumeComponent.horizontalBlur.overrideState ?
volumeComponent.horizontalBlur.value : defaultSettings.horizontalBlur;
float verticalBlur = volumeComponent.verticalBlur.overrideState ?
volumeComponent.verticalBlur.value : defaultSettings.verticalBlur;
material.SetFloat(horizontalBlurId, horizontalBlur);
material.SetFloat(verticalBlurId, verticalBlur);
}
```
5. In the Unity scene, create a [local Box Volume](../Volumes.md). If a [Volume Profile](../Volume-Profile.md) is missing, create a new one by clicking **New** next to the **Profile** property. Add the `Custom Volume Component` [override](../VolumeOverrides.md) to the Volume.
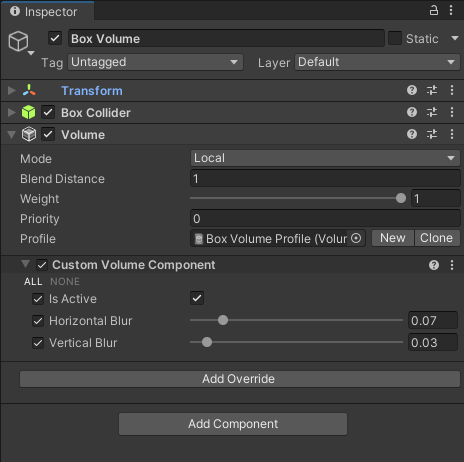
6. Enable the settings in the `Custom Volume Component` override and set the values for this Volume. Move the Volume so that the camera is inside it. The settings from the Volume override the default settings from the custom renderer feature.
## All complete code for the scripts in this example
This section contains the complete code for all the scripts in this example.
### Custom Renderer Feature code
Below is the complete code for the custom Renderer Feature script.
```C#
using System;
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal;
public class BlurRendererFeature : ScriptableRendererFeature
{
[SerializeField] private BlurSettings settings;
[SerializeField] private Shader shader;
private Material material;
private BlurRenderPass blurRenderPass;
public override void Create()
{
if (shader == null)
{
return;
}
material = new Material(shader);
blurRenderPass = new BlurRenderPass(material, settings);
blurRenderPass.renderPassEvent = RenderPassEvent.BeforeRenderingPostProcessing;
}
public override void AddRenderPasses(ScriptableRenderer renderer,
ref RenderingData renderingData)
{
if (renderingData.cameraData.cameraType == CameraType.Game)
{
renderer.EnqueuePass(blurRenderPass);
}
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
#if UNITY_EDITOR
if (EditorApplication.isPlaying)
{
Destroy(material);
}
else
{
DestroyImmediate(material);
}
#else
Destroy(material);
#endif
}
}
[Serializable]
public class BlurSettings
{
[Range(0, 0.4f)] public float horizontalBlur;
[Range(0, 0.4f)] public float verticalBlur;
}
```
### Custom render pass code
Below is the complete code for the custom Render Pass script.
```C#
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Rendering;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.RenderGraphModule;
using UnityEngine.Rendering.Universal;
public class BlurRenderPass : ScriptableRenderPass
{
private static readonly int horizontalBlurId = Shader.PropertyToID("_HorizontalBlur");
private static readonly int verticalBlurId = Shader.PropertyToID("_VerticalBlur");
private const string k_BlurTextureName = "_BlurTexture";
private const string k_VerticalPassName = "VerticalBlurRenderPass";
private const string k_HorizontalPassName = "HorizontalBlurRenderPass";
private static Vector4 m_ScaleBias = new Vector4(1f, 1f, 0f, 0f);
private BlurSettings defaultSettings;
private Material material;
private RenderTextureDescriptor blurTextureDescriptor;
public BlurRenderPass(Material material, BlurSettings defaultSettings)
{
this.material = material;
this.defaultSettings = defaultSettings;
blurTextureDescriptor = new RenderTextureDescriptor(Screen.width, Screen.height,
RenderTextureFormat.Default, 0);
}
private void UpdateBlurSettings()
{
if (material == null) return;
// Use the Volume settings or the default settings if no Volume is set.
var volumeComponent =
VolumeManager.instance.stack.GetComponent();
float horizontalBlur = volumeComponent.horizontalBlur.overrideState ?
volumeComponent.horizontalBlur.value : defaultSettings.horizontalBlur;
float verticalBlur = volumeComponent.verticalBlur.overrideState ?
volumeComponent.verticalBlur.value : defaultSettings.verticalBlur;
material.SetFloat(horizontalBlurId, horizontalBlur);
material.SetFloat(verticalBlurId, verticalBlur);
}
private class PassData
{
internal TextureHandle src;
internal Material material;
}
private static void ExecutePass(PassData data, RasterGraphContext context, int pass)
{
Blitter.BlitTexture(context.cmd, data.src, m_ScaleBias, data.material, pass);
}
public override void RecordRenderGraph(RenderGraph renderGraph,
ContextContainer frameData)
{
UniversalResourceData resourceData = frameData.Get();
UniversalCameraData cameraData = frameData.Get();
// The following line ensures that the render pass doesn't blit
// from the back buffer.
if (resourceData.isActiveTargetBackBuffer)
return;
// Set the blur texture size to be the same as the camera target size.
blurTextureDescriptor.width = cameraData.cameraTargetDescriptor.width;
blurTextureDescriptor.height = cameraData.cameraTargetDescriptor.height;
blurTextureDescriptor.depthBufferBits = 0;
TextureHandle srcCamColor = resourceData.activeColorTexture;
TextureHandle dst = UniversalRenderer.CreateRenderGraphTexture(renderGraph,
blurTextureDescriptor, k_BlurTextureName, false);
// Update the blur settings in the material
UpdateBlurSettings();
// This check is to avoid an error from the material preview in the scene
if (!srcCamColor.IsValid() || !dst.IsValid())
return;
// Vertical blur pass
using (var builder = renderGraph.AddRasterRenderPass(k_VerticalPassName,
out var passData))
{
// Configure pass data
passData.src = srcCamColor;
passData.material = material;
// Configure render graph input and output
builder.UseTexture(passData.src);
builder.SetRenderAttachment(dst, 0);
// Blit from the camera color to the render graph texture,
// using the first shader pass.
builder.SetRenderFunc((PassData data, RasterGraphContext context) => ExecutePass(data, context, 0));
}
// Horizontal blur pass
using (var builder = renderGraph.AddRasterRenderPass(k_HorizontalPassName, out var passData))
{
// Configure pass data
passData.src = dst;
passData.material = material;
// Use the output of the previous pass as the input
builder.UseTexture(passData.src);
// Use the input texture of the previous pass as the output
builder.SetRenderAttachment(srcCamColor, 0);
// Blit from the render graph texture to the camera color,
// using the second shader pass.
builder.SetRenderFunc((PassData data, RasterGraphContext context) => ExecutePass(data, context, 1));
}
}
}
```
### Volume Component code
Below is the complete code for the Volume Component script.
```C#
using System;
using UnityEngine.Rendering;
[Serializable]
public class CustomVolumeComponent : VolumeComponent
{
public BoolParameter isActive = new BoolParameter(true);
public ClampedFloatParameter horizontalBlur =
new ClampedFloatParameter(0.05f, 0, 0.5f);
public ClampedFloatParameter verticalBlur =
new ClampedFloatParameter(0.05f, 0, 0.5f);
}
```
## The custom shader for the blur effect
This section contains the code for the custom shader that implements the blur effect.
```c++
Shader "CustomEffects/Blur"
{
HLSLINCLUDE
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.universal/ShaderLibrary/Core.hlsl"
// The Blit.hlsl file provides the vertex shader (Vert),
// the input structure (Attributes), and the output structure (Varyings)
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.core/Runtime/Utilities/Blit.hlsl"
float _VerticalBlur;
float _HorizontalBlur;
float4 BlurVertical (Varyings input) : SV_Target
{
const float BLUR_SAMPLES = 64;
const float BLUR_SAMPLES_RANGE = BLUR_SAMPLES / 2;
float3 color = 0;
float blurPixels = _VerticalBlur * _ScreenParams.y;
for(float i = -BLUR_SAMPLES_RANGE; i <= BLUR_SAMPLES_RANGE; i++)
{
float2 sampleOffset = float2 (0, (blurPixels / _BlitTexture_TexelSize.w) * (i / BLUR_SAMPLES_RANGE));
color += SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(_BlitTexture, sampler_LinearClamp, input.texcoord + sampleOffset).rgb;
}
return float4(color.rgb / (BLUR_SAMPLES + 1), 1);
}
float4 BlurHorizontal (Varyings input) : SV_Target
{
const float BLUR_SAMPLES = 64;
const float BLUR_SAMPLES_RANGE = BLUR_SAMPLES / 2;
UNITY_SETUP_STEREO_EYE_INDEX_POST_VERTEX(input);
float3 color = 0;
float blurPixels = _HorizontalBlur * _ScreenParams.x;
for(float i = -BLUR_SAMPLES_RANGE; i <= BLUR_SAMPLES_RANGE; i++)
{
float2 sampleOffset =
float2 ((blurPixels / _BlitTexture_TexelSize.z) * (i / BLUR_SAMPLES_RANGE), 0);
color += SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(_BlitTexture, sampler_LinearClamp, input.texcoord + sampleOffset).rgb;
}
return float4(color / (BLUR_SAMPLES + 1), 1);
}
ENDHLSL
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" "RenderPipeline" = "UniversalPipeline"}
LOD 100
ZWrite Off Cull Off
Pass
{
Name "BlurPassVertical"
HLSLPROGRAM
#pragma vertex Vert
#pragma fragment BlurVertical
ENDHLSL
}
Pass
{
Name "BlurPassHorizontal"
HLSLPROGRAM
#pragma vertex Vert
#pragma fragment BlurHorizontal
ENDHLSL
}
}
}
```