8.7 KiB
Cinemachine Free Look Camera
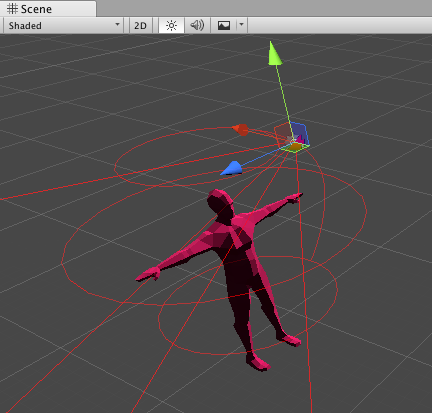
The Cinemachine Free Look Camera component provides a third-person camera experience. This Cinemachine Virtual Camera orbits around its subject along a position specified by three separate camera rigs: Top, Middle, and Bottom.
Each rig defines a ring around the target, with its own radius, height offset, composer, lens properties, and Noise settings. These are the same as the properties for a regular Virtual Camera.
Cinemachine Free Look Camera also defines a spline that connects the rigs. The spline defines the camera’s position when blending between the rigs.
Free Look uses player input along the x and y axes. The x axis controls the orbital position along the Top, Middle, or Bottom horizontal orbits, like the Orbital Transposer. The y-axis controls the vertical position, using the spline to determine the position between rigs.
Properties:
| Property: | Function: | |
|---|---|---|
| Solo | Toggles whether or not the Virtual Camera is temporarily live. Use this property to get immediate visual feedback in the Game view to adjust the Virtual Camera. | |
| Game Window Guides | Toggles the visibility of compositional guides in the Game view. These guides are available when Look At specifies a GameObject and the Aim section uses Composer or Group Composer, or when Follow specifies a target and the Body section uses Framing Composer. This property applies to all Virtual Cameras. | |
| Save During Play | Check to apply the changes while in Play mode. Use this feature to fine-tune a Virtual Camera without having to remember which properties to copy and paste. This property applies to all Virtual Cameras. | |
| Priority | The importance of this Virtual Camera for choosing the next shot. A higher value indicates a higher priority. Cinemachine Brain chooses the next live Virtual Camera from all Virtual Cameras that are activated and have the same or higher priority as the current live Virtual Camera. This property has no effect when using a Virtual Camera with Timeline. | |
| Follow | The target GameObject to move with. The Body properties use this target to update the position of the Unity camera. | |
| Look At | The target GameObject to aim at. The Aim properties use this target to update the rotation of the Unity camera. This property is normally the same as the Follow target. | |
| Common Lens | Check to apply a common lens setting to all three child rigs. Uncheck to use separate lens settings for each child rig. | |
| Lens | If Common Lens is checked, these lens settings apply to all three rigs. These properties mirror their counterparts in the property settings for the Unity camera. | |
| Vertical FOV | This is the camera view in vertical degrees. For example, to specify the equivalent of a 50mm lens on a Super 35 sensor, enter a Field of View of 19.6 degrees. This property is available when the Unity camera with the Cinemachine Brain component uses a Projection of Perspective. | |
| Orthographic Size | When using an orthographic camera, this defines the half-height, in world coordinates, of the camera view. This property is available when the Unity camera with the Cinemachine Brain component uses a Projection of Orthographic. | |
| Near Clip Plane | The closest point relative to the camera where drawing occurs. | |
| Far Clip Plane | The furthest point relative to the camera where drawing occurs. | |
| Dutch | Dutch angle. Tilts the Unity camera on the Z axis, in degrees. This property is unique to the Virtual Camera; there is no counterpart property in the Unity camera. | |
| Transitions | ||
| Blend Hint | How to blend to and from the Free Look camera. Use None for default linear interpolation of position and aim. Use Spherical Position to blend spherically about the Look At position, linearly blending between Look At targets. Use Cylindrical Position to blend in a cylindrical path around the Look At target and interpolate linearly on the vertical axis. Use Screen Space Aim When Targets Differ for a standard linear position blend, with screen-space angular blend between differing Look At targets. | |
| Inherit Position | When this virtual camera goes Live, attempt to force the position to be the same as the current position of the Unity Camera, allowing the virtual camera to apply its damping to accomplish the blend | |
| Camera Activated | This event is invoked when the Virtual Camera becomes live. Attach custom handlers here if you need them. | |
| Y Axis, X Axis | The vertical and horizontal axes for blending between rigs. For Y Axis the Value range is 0 to 1 and represents the blend position between the Top, Middle, and Bottom rigs. The value 0.5 represents the middle rig. For X Axis, the Value is the angular deviation (in degrees) of the camera from directly behind the target. | |
| Max Speed | The maximum speed of this axis in degrees/second, or the multipler for the input value if Speed Mode is set to InputValueGain. | |
| Speed Mode | How the axis responds to input. MaxSpeed (the default) clamps the maximum speed at which the axis can change, regardless of the input. Input Value Gain multiplies the input value by MaxSpeed. | |
| Accel Time | The amount of time in seconds to accelerate to Max Speed. | |
| Decel Time | The amount of time in seconds to decelerate to zero. | |
| Input Axis Name | The name of this axis as specified in Unity Input manager. Setting to an empty string disables the automatic updating of the axis. | |
| Input Axis Value | The value of the input axis. A value of 0 means no input. To drive this directly, use a custom input system. Or you set the Axis Name to control the value with the Unity Input Manager. | |
| Invert | Check to invert the raw value of the input axis. The X Axis and Y Axis have opposite defaults. Checking this box causes the view to move opposite the input for the X Axis. Checking the box for the Y Axis causes the view to move in the same direction as the input. | |
| Y Axis Recentering | Controls the automatic recentering on the y axis. | |
| Enabled | Check to enable automatic recentering. | |
| Wait Time | When no user input has been detected on the axis, the camera waits this long in seconds before recentering. | |
| Recentering Time | Maximum angular speed of recentering. Accelerates into and decelerates out of the centered position. | |
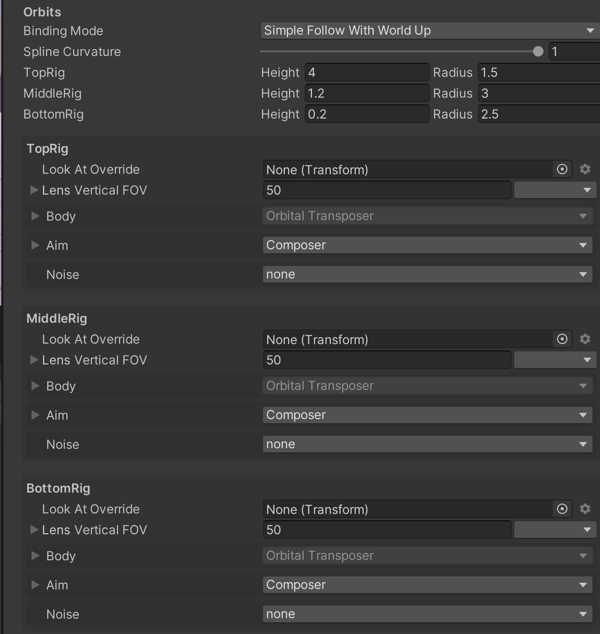
| Orbits | Properties for defining the Top, Middle, and Bottom rigs. | |
| Binding Mode | The coordinate space to use to interpret the offset from the target. | |
| Lock To Target On Assign | Makes the orientation of the virtual camera match the local frame of the Follow target, at the moment when the virtual camera is activated or when the target is assigned. This offset remains constant in world space. The camera does not rotate along with the target. | |
| Lock To Target With World Up | Makes the virtual camera use the local frame of the Follow target with tilt and roll set to 0. This binding mode ignores all target rotations except yaw. | |
| Lock To Target No Roll | Makes the virtual camera use the local frame of the Follow target, with roll set to 0. | |
| Lock To Target | Makes the virtual camera use the local frame of the Follow target. When the target rotates, the camera moves with it to maintain the offset and to maintain the same view of the target. | |
| World Space | The offset is interpreted in world space relative to the origin of the Follow target. The camera will not change position when the target rotates. | |
| Simple Follow With World Up | Simple follow with world up interprets the offset and damping values in camera-local space. This mode emulates the action a human camera operator would take when instructed to follow a target. The camera attempts to move as little as possible to maintain the same distance from the target; the direction of the camera with regard to the target does not matter. Regardless of the orientation of the target, the camera tries to preserve the same distance and height from it. | |
| Spline Curvature | The tautness of the line that connects the rigs’ orbits. This line determines the final placement on the y axis. | |
| Height, Radius | The radius and height of the Top, Middle, and Bottom rigs relative to the Follow target. |